Hobb's Internet Timeline
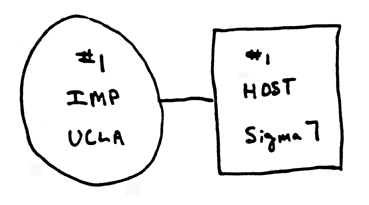
Source: www.zakon.orgHobb's Internet Timeline v 6.1 traces the history of internet from 1957 onwards. The first RFC was piblished in 1969. It was for a Host Software.Look at the first diagram of host to IMP connection- a far cry from the present scenario.

From 1970's the timeline gives year by year progress of the developments. The protocol TCP was split into TCP and Ip in 1978.
The installation of ARPANET(earlier version of Internet) was made in 1969 and became operational in 1971.
In 1981 BITNET "Because It's Time NETwork"
Started as a cooperative network at the City University of New York, with the first connection to Yale.
Original acronym stood for 'There' instead of 'Time' in reference to the free NJE protocols provided with the IBM systems .
Provides electronic mail and listserv servers to distribute information, as well as file transfers
Some milestones
1984 DNS was introduced
1986 IETF and IRTF came into existence
1987 Hosts reached a figure 0f 10000
1000th RFC
1988 Internet assigned Numbers Authority established.
1989 Number of hosts 100000, ie 10 fold increase in two years.
1990 ARPANET ceases to exist. Archie released by Peter Deutsch, Alan Emtage, and Bill Heelan at McGill
The World comes on-line (world.std.com), becoming the first commercial provider of Internet dial-up access .
RFC 1178 : choosing a name for your computer
1991 Wide Area Information Servers (WAIS), invented by Brewster Kahle, released by Thinking Machines Corporation.
Gopher released by Paul Lindner and Mark P. McCahill from the Univ of Minnesota
World-Wide Web (WWW) released by CERN; Tim Berners-Lee developer
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) released by Philip Zimmerman
1992 The term "surfing the Internet" is coined by Jean Armour Polly
Zen and the Art of the Internet is published by Brendan Kehoe
1993 US White House comes on-line (http://www.whitehouse.gov/):
1994 IPng recommended by IETF at its Toronto meeting (July) and approved by IESG in November. Later documented as RFC 1752
RFC 1605: SONET to Sonnet Translation
RFC 1606: A Historical Perspective On The Usage Of IP Version 9
1995 RFC 1607: A VIEW FROM THE 21ST CENTURY
Sun launches JAVA on May 23
1996 The Internet Ad Hoc Committee announces plans to add 7 new generic Top Level Domains (gTLD): .firm, .store, .web, .rec ,.arts, .info, .nom. The IAHC plan also calls for a competing group of domain registrars worldwide.
Technologies of the Year: Search engines, JAVA, Internet Phone
Emerging Technologies: Virtual environments (VRML), Collaborative tools, Internet appliance (Network Computer)
1997 2000th RFC: "Internet Official Protocol Standards" . 1000 RFCs in 10 years.
Technologies of the Year: Push, Multicasting
Emerging Technologies: Push
1998 Hobbes' Internet Timeline is released as RFC 2235 & FYI 32
Web size estimates range between 275 (Digital) and 320 (NEC) million pages for 1Q
Open source software comes of age
Technologies of the Year: E-Commerce, E-Auctions, Portals
Emerging Technologies: E-Trade, XML, Intrusion Detection
1999 RFC 2555: 30 Years of RFCs
RFC 2626: The Internet and the Millennium Problem (Year 2000)
Technologies of the Year: E-Trade, Online Banking, MP3
Emerging Technologies: Net-Cell Phones, Thin Computing, Embedded Computing
Viruses of the Year: Melissa (March), ExploreZip (June)
2000 Web size estimates by NEC-RI and Inktomi surpass 1 billion indexable pages
RFC 2795: The Infinite Monkey Protocol Suite
Hacks of the Year: RSA Security (Feb), Apache (May), Western Union (Sep), Microsoft (Oct)
Technologies of the Year: ASP, Napster
Emerging Technologies: Wireless devices, IPv6
Viruses of the Year: Love Letter (May)
2001 First uncompressed real-time gigabit HDTV transmission across a wide-area IP network takes place on Internet2 (12 Nov)
Emerging Technologies: Grid Computing, P2P
.biz and .info are added to the root server on 27 June with registrations beginning in July. .biz domain go live on 7 Nov.
2002 Global Terabit Research Network (GTRN) is formed composed of two OC-48 2.4GB circuits connecting Internet2 Abiline, CANARIE CA*net3, and GÉANT (18 Feb)
RFC 3251: Electricity over IP
2003 RFC 3514: The Security Flag in the IPv4 Header (The Evil Bit)
Public Interest Registry (PIR) takes over as .org registry operator on 1 Jan. Transition is completed on 27 Jan. By giving up .org VeriSign is able to retain control over .com domains
The growth of no of hosts in the net saw an exponential increase from the year 1997 onwards. It was roughly 2 crores in 1997. Now it is over 20 crores.